
(Source Image: NVIDIA)
NVIDIA’s GPU Technology Conference (GTC) 2025 is one of the most anticipated tech events, bringing together industry leaders, AI researchers, developers, and enterprises to explore the latest advancements in AI, deep learning, cloud computing, robotics, and next-gen GPUs. Led by NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang, the keynote showcased groundbreaking innovations in AI, data centers, autonomous systems, and gaming technologies.
This year’s event was particularly crucial as AI adoption is accelerating across industries. With the rise of AI-driven applications, generative AI, and high-performance computing, NVIDIA is expected to introduce next-generation GPUs and cutting-edge AI frameworks that will define the future of computing.
Whether you’re a developer, researcher, or tech enthusiast, this event has definitely provided insights into the technologies shaping the future. Below are the main highlights that you simply must not miss:
1. Newton

(Source Image: NVIDIA)
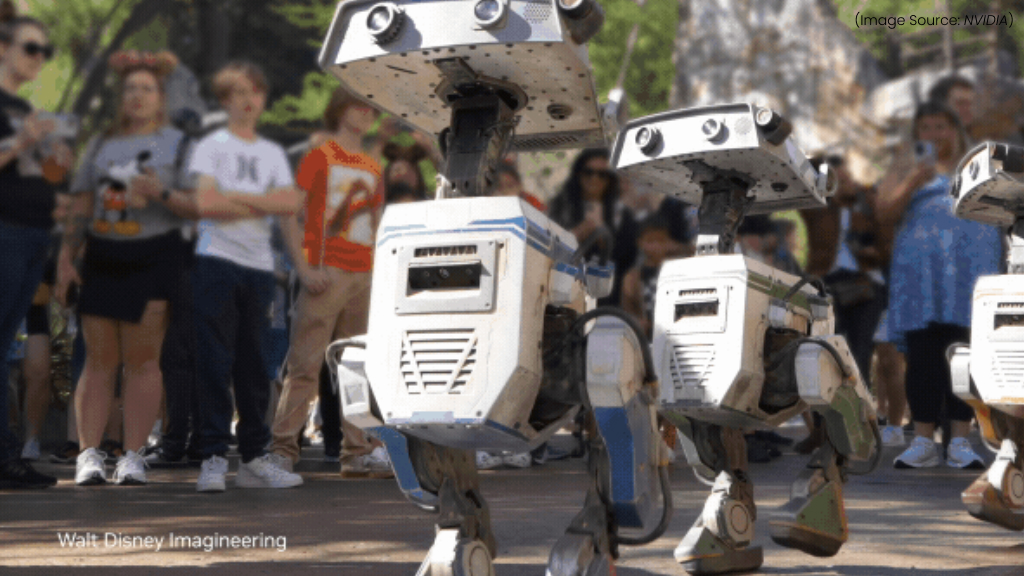
Newton is an advanced open-source physics engine developed collaboratively by NVIDIA, Google DeepMind, and Disney Research. Announced at NVIDIA GTC 2025, Newton is designed to enhance robotics simulation, AI training, and real-world physics modeling, making it a powerful tool for developing intelligent humanoid robots and autonomous systems.
Newton enables real-time physics simulations with features such as rigid body dynamics, soft body simulations, and articulated joints, allowing developers to test robotic behaviors in a virtual environment before deploying them in the real world. This reduces the need for expensive physical prototypes and accelerates innovation in robotic control, reinforcement learning, and AI-driven automation.
Newton is built on NVIDIA’s Warp framework, optimized for AI and GPU acceleration, allowing developers to train robotic models in simulation. By supporting GPU acceleration and multi-threaded processing, it ensures high-performance simulations for complex robotic systems.
Newton is compatible with frameworks like MuJoCo Playground and NVIDIA Isaac Lab, allowing developers to reuse existing models and code for efficient adaptation across different engines. It supports multiphysics environments, enabling simulations of diverse materials such as cloth, sand, and deformable objects. This extensibility is enhanced by custom solvers and integrators for complex interactions.
2. GROOT N1
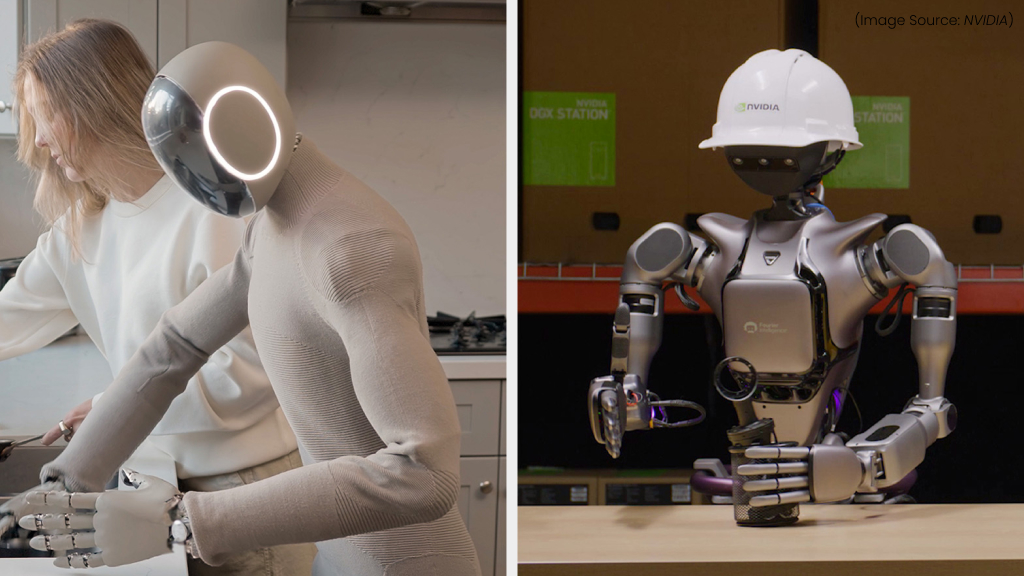
(Source Image: NVIDIA)
GR00T N1 is a groundbreaking open-source humanoid robot foundation model designed for customization, AI integration, and real-world adaptability. As the first of its kind, it provides a modular framework that allows researchers, developers, and roboticists to train, modify, and enhance humanoid robotics with advanced AI capabilities, natural language processing, and real-time decision-making.
GR00T N1 is built on an open-source architecture, enabling the global robotics community to collaborate, optimize, and innovate. It supports custom AI models, sensor integrations, and real-world learning, making it an ideal platform for applications in healthcare, automation, assistive robotics, and human-robot interaction.
With support for deep learning, reinforcement learning, and real-time motion control, GR00T N1 can be tailored for various tasks, from complex industrial automation to companion robotics. Its fully customizable nature ensures that developers can continually improve its functionality without proprietary restrictions.
By democratizing humanoid robotics, GR00T N1 is paving the way for the future of intelligent, adaptive robots, accelerating innovation in AI-driven robotics research.
3. Blue

(Source Image: NVIDIA)
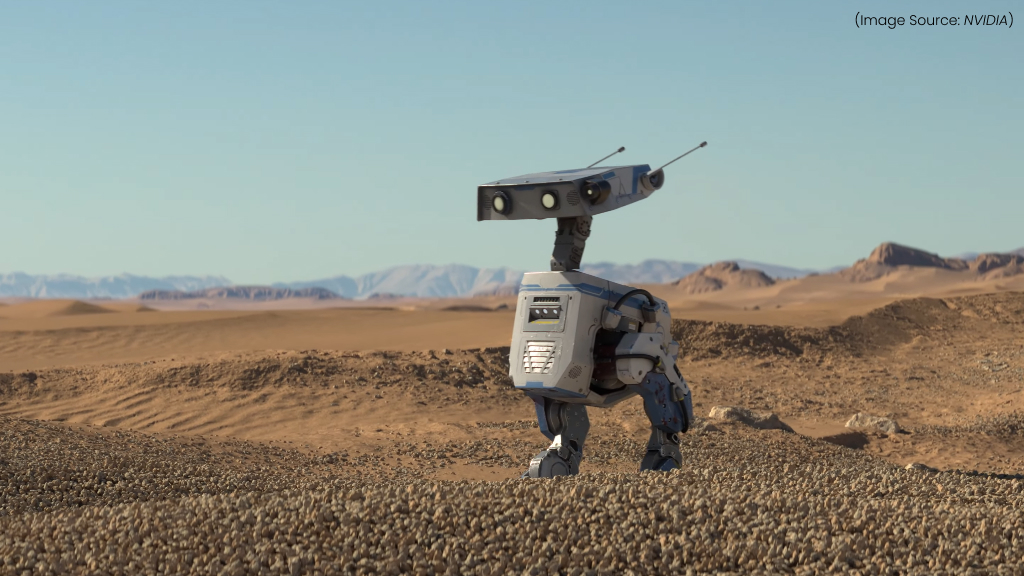
NVIDIA’s Blue is an advanced AI-driven humanoid robot designed to push the boundaries of robotics, deep learning, and real-world automation. Developed as part of NVIDIA’s efforts to accelerate robotics research, Blue integrates cutting-edge AI models, GPU-powered simulations, and real-time reinforcement learning, making it a significant step toward the future of intelligent robotics.
Blue is built with soft, adaptive hardware, allowing it to interact safely with humans and objects. It leverages deep reinforcement learning and NVIDIA’s Isaac Sim platform to continuously improve its motion control, object manipulation, and problem-solving capabilities. This makes Blue an ideal solution for applications in automation, healthcare, and AI research.
With open-source tools and developer-friendly APIs, NVIDIA’s Blue fosters a collaborative robotics ecosystem, enabling researchers and engineers to customize and train AI models for diverse tasks. Its ability to learn from simulations and real-world interactions positions it as a next-generation robotic assistant capable of performing complex functions with human-like dexterity.
As AI-driven robotics continues to evolve, NVIDIA’s Blue stands as a key innovation, bridging the gap between cutting-edge AI research and real-world robotic applications. It does feature dual onboard computing systems to handle real-time AI processing and motion control.
4. DGX Spark

(Source Image: NVIDIA)
NVIDIA DGX Spark is a compact AI supercomputer designed to democratize access to high-performance computing for AI development, and is powered by the NVIDIA GB10 Grace Blackwell architecture. This makes it particularly suitable for tasks like fine-tuning and inference of large AI models.
The system features 128 GB of LPDDR5x memory with a bandwidth of 273 GB/s, ensuring rapid data access for demanding workloads. It supports up to 4 TB of SSD storage, providing ample space for datasets and applications. Connectivity options include WiFi 7, Bluetooth, and multiple USB4 ports, enhancing its versatility in various environments.
DGX Spark is compatible with advanced AI models such as the NVIDIA Cosmos Reason and GR00T N1. This system is aimed at researchers, data scientists, and developers, allowing them to prototype complex AI applications directly from their desktops while maintaining the ability to scale up to larger infrastructures as needed.
5. NVIDIA Drive

(Source Image: NVIDIA)
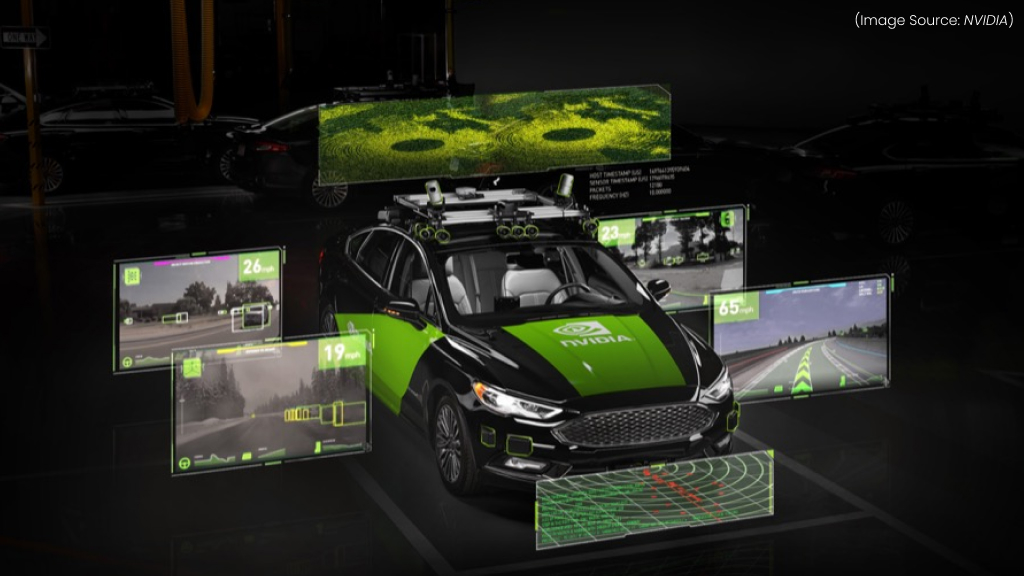
NVIDIA DRIVE is an advanced autonomous vehicle (AV) platform designed to facilitate the development and deployment of self-driving technologies. It encompasses a full-stack solution that supports automated driving, active safety, parking, and AI cockpit capabilities, scaling from Level 2+ to Level 5 automation.
The platform integrates the NVIDIA DRIVE Hyperion sensor suite, which includes multiple cameras, radars, and ultrasonic sensors to provide comprehensive 360-degree environmental awareness. This suite is essential for developing robust AV systems capable of interpreting complex driving scenarios.
NVIDIA DRIVE also includes the DRIVE OS, a sophisticated operating system that enables real-time data processing from various sensors, ensuring vehicles can make rapid decisions in dynamic environments. With a focus on safety and scalability, NVIDIA DRIVE is poised to revolutionize transportation across various sectors, including logistics and agriculture.
6. DGX Station
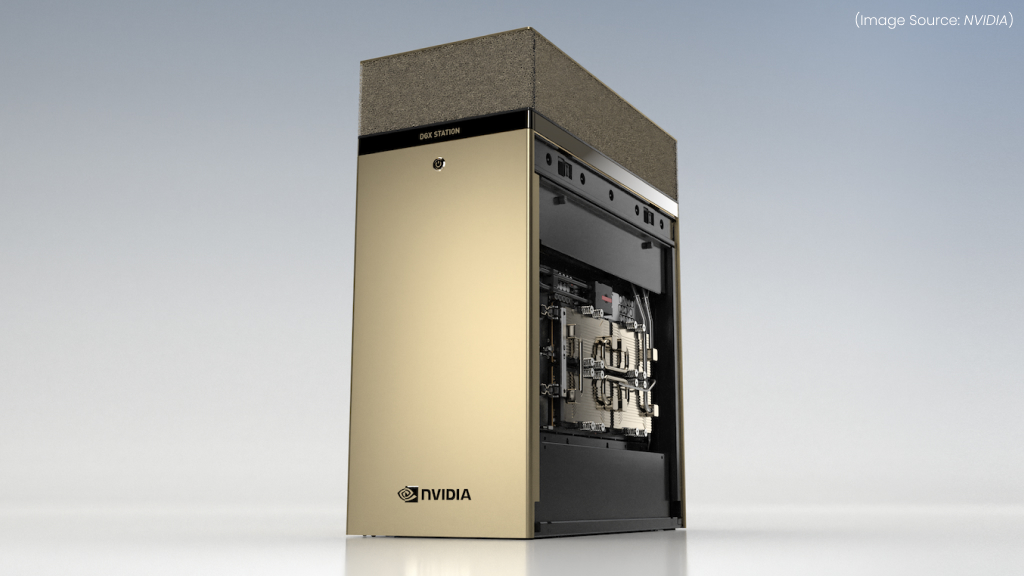

(Source Image: NVIDIA)
The NVIDIA DGX Station is a high-performance AI workstation designed to bring supercomputing power to researchers, data scientists, and enterprises without the need for a dedicated data center. DGX Station delivers data center-level AI performance in a compact, plug-and-play form factor, making it ideal for AI model training, deep learning, and scientific computing.
The DGX Station includes NVLink interconnect technology, ensuring ultra-fast data transfers between GPUs for seamless model training and inference. The Station operates with an advanced cooling system, making it suitable for office and lab environments. It also supports cloud-native AI workflows, allowing researchers to work efficiently across cloud-based AI infrastructures.
By providing supercomputing performance in a standalone workstation, NVIDIA DGX Station enables organizations to build and deploy cutting-edge AI models without requiring large-scale infrastructure. It is a powerful tool for AI research, medical imaging, finance, and scientific innovation.
7. NVIDIA Isaac for Healthcare
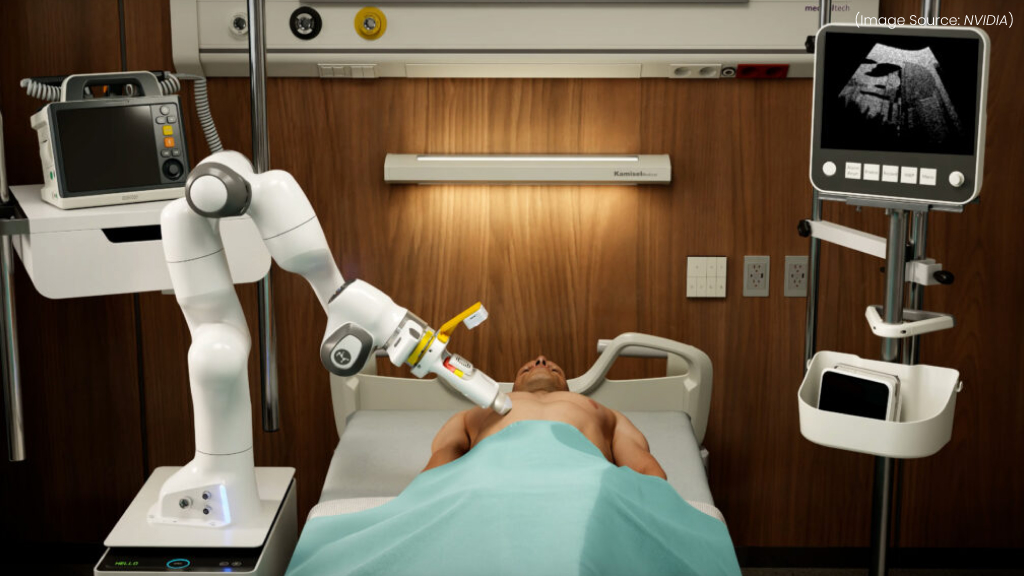
(Source Image: NVIDIA)
NVIDIA Isaac is transforming healthcare robotics by enabling AI-driven automation, precision surgery, and intelligent patient care. Built on NVIDIA’s GPU-accelerated AI computing, Isaac provides simulation, deep learning, and real-time robotics control, making medical robots smarter, safer, and more efficient.
By combining NVIDIA Isaac with deep learning and robotic simulation, hospitals and research labs can train and deploy AI-powered robots faster, ensuring safer, more precise medical procedures and better patient outcomes. As AI-driven healthcare robotics advances, NVIDIA Isaac is at the forefront of revolutionizing medical technology for a smarter, more automated future.
8. NEO Gamma Vacuuming
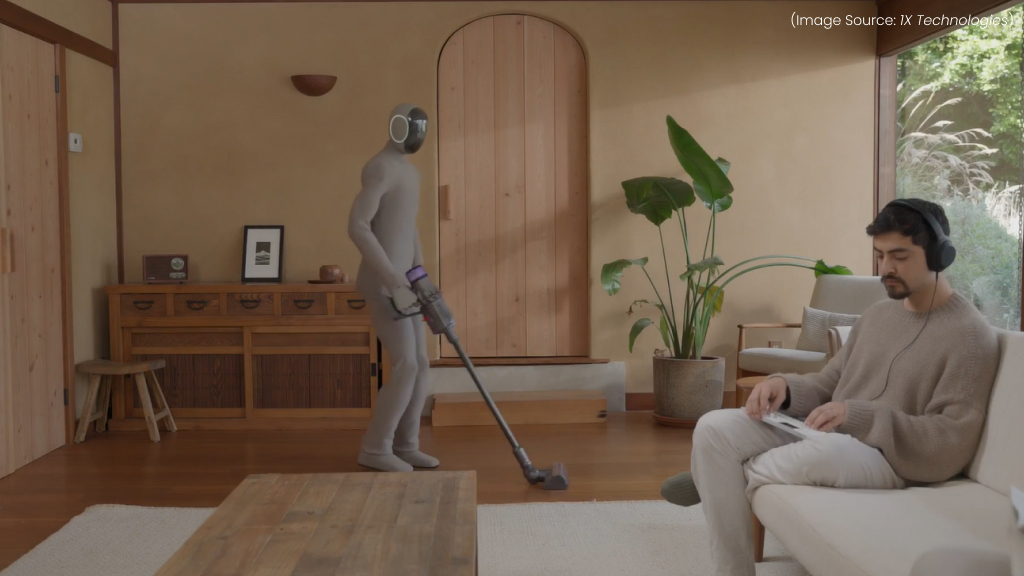

(Source Image: 1X Technologies)
At NVIDIA GTC, attendees witnessed an advanced AI-powered autonomous cleaning robot, NEO Gamma, efficiently vacuuming and maintaining the event space. Designed for smart automation in commercial environments, NEO Gamma utilizes NVIDIA’s AI-driven robotics technology to navigate complex spaces, detect obstacles, and optimize cleaning efficiency.
Equipped with advanced sensors, computer vision, and deep learning algorithms, NEO Gamma autonomously maps its surroundings and adjusts its cleaning patterns in real time. Using AI-powered object recognition, it can detect spills, debris, and high-traffic areas, ensuring thorough and efficient vacuuming without human intervention.
As AI-driven automation continues to evolve, robots like NEO Gamma highlight NVIDIA’s role in advancing real-world robotics applications, paving the way for smarter, more efficient AI-powered solutions in everyday tasks.
9. Atlas
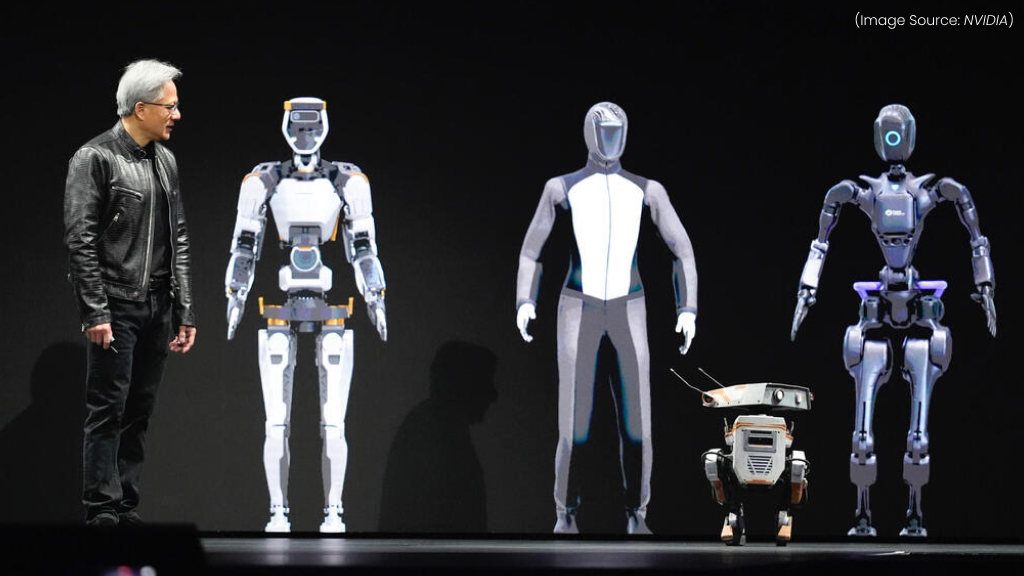
(Source Image: NVIDIA)
At NVIDIA GTC , Atlas, a cutting-edge humanoid robot, was showcased in both real and simulated environments. Powered by AI, deep learning, and NVIDIA’s Isaac robotics platform, Atlas demonstrates remarkable agility, real-time decision-making, and human-like motion control.
Atlas has undergone extensive training that allows for realistic physics modeling, reinforcement learning, and AI-driven decision-making. In this virtual space, Atlas learns to navigate obstacles, interact with objects, and refine its movement strategies without physical risks or constraints.
In the physical world, Atlas applies its simulated learning to perform complex tasks, such as autonomous navigation, and industrial automation. Equipped with computer vision, AI-powered sensors, and adaptive control systems, Atlas showcases its ability to work alongside humans in factories, warehouses, and service industries.
10. Blackwell Ultra
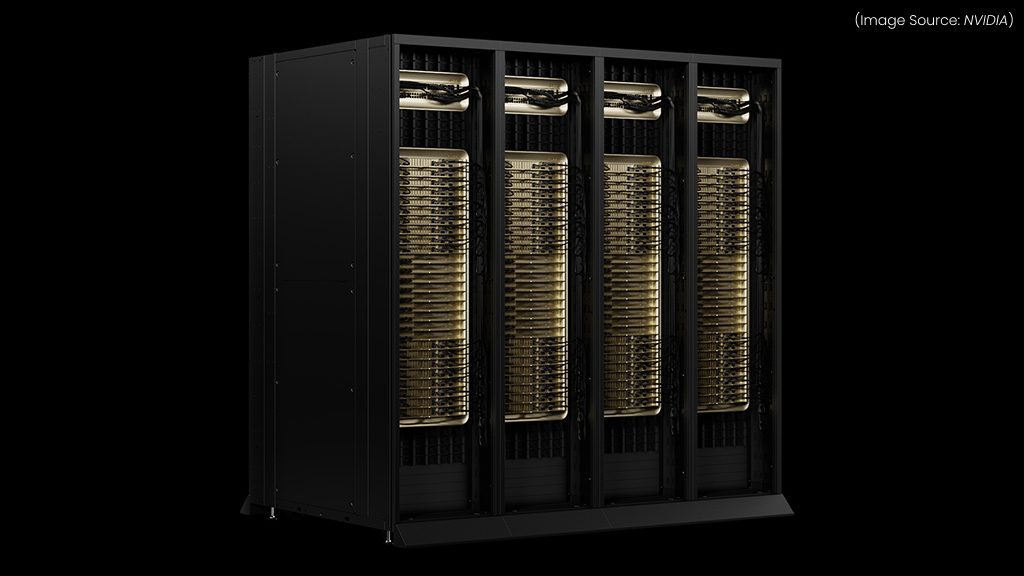

(Source Image: NVIDIA)
At the recent NVIDIA GTC conference, NVIDIA unveiled Blackwell Ultra, the latest evolution of its AI factory platform, marking a significant advancement in AI reasoning capabilities. Building upon the foundation of the original Blackwell architecture, Blackwell Ultra introduces enhanced performance features tailored for complex AI workloads.
Blackwell Ultra boosts both training and test-time scaling inference, enabling organizations to accelerate applications such as AI reasoning, agentic AI, and physical AI. Blackwell Ultra optimizes memory utilization, which is crucial for managing large-scale AI models without compromising performance.
The introduction of Blackwell Ultra signifies NVIDIA’s commitment to advancing AI infrastructure, providing tools that enhance real-time, multi-agent AI system pipelines and long-context reasoning. This platform is poised to empower organizations in developing more sophisticated and efficient AI applications across various industries.














